Geothermal Systems
Cost-Effective. Energy Efficient. Environmentally Clean.
Heating and Cooling Systems Installation and Service
As an early adopter of geothermal heating and cooling, we bring over 15 years of experience to heating and cooling geothermal technology projects. We are licensed contractors experienced with both commercial and residential applications.
Five important facts to remember are that…
- It is very widespread and there are more than 1,000,000 homes using geothermal heating and cooling in the United States.
- Geothermal heating and cooling is being used by school buildings and other structures.
- There are two primary advantages: economical and environmental.
- Economic advantages – geothermal systems reduce heating and cooling expenses by 40% and more.
- Environmental advantages – current geothermal installations are eliminating more than 5.8 metric tons of CO2 annually.
How Geothermal Heat Pump Works
Quite simply put, geothermal heating and cooling uses heat from the earth to heat and cool a structure, whether it be a home, office building, or other structure. These systems are the most energy efficient, environmentally clean, and cost-effective space conditioning systems available according to the Environmental Protection Agency. View the video to the right to learn more about how it works.
Call For a Quote:
(908) 454-4043
Geothermal Heating and Cooling
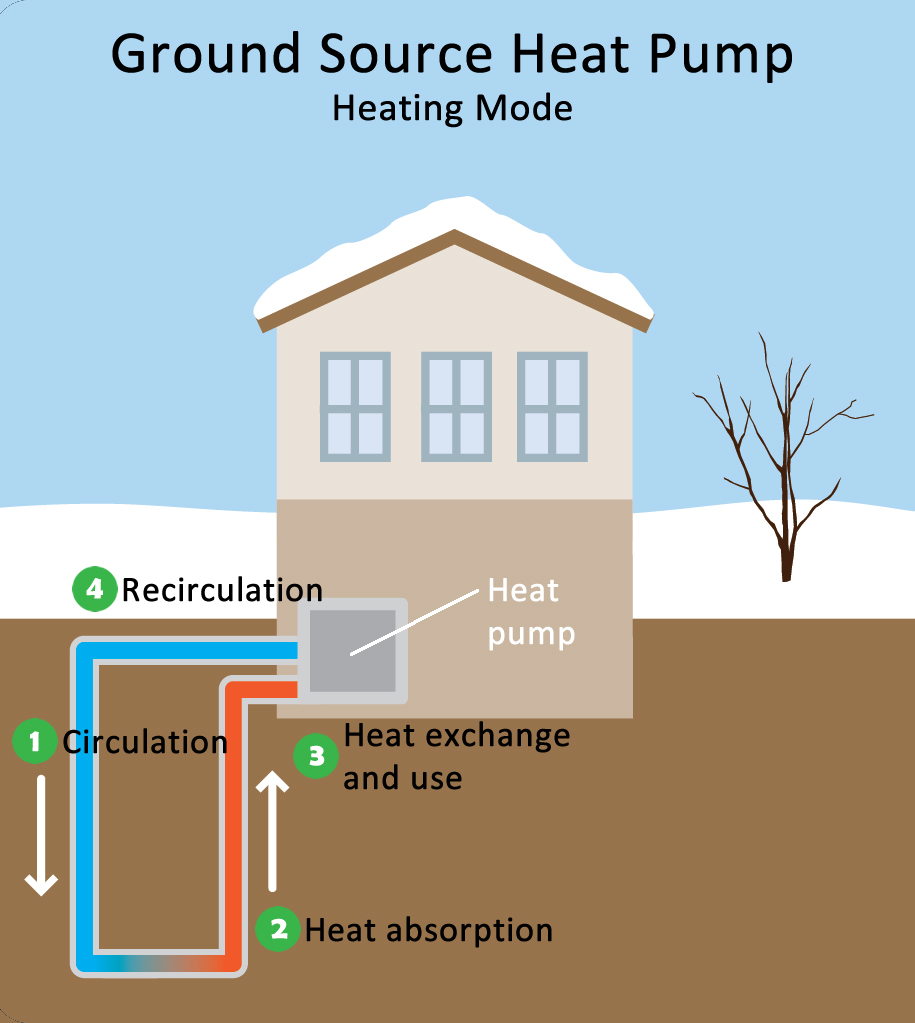
Geothermal - Heating Mode
The heating process involves the extraction of heat energy from the ground, and moving it into the building. Transferring the heat from the earth to the building involves a cycle of evaporation, compression, condensation and expansion. A refrigerant is used as the heat transfer medium. The heating cycle starts as cold, liquid refrigerant passes through a water-to-refrigerant heat exchanger and absorbs heat from the low temperature source (earth loop fluid or well water). The refrigerant evaporates into a gas as heat is absorbed. The gaseous refrigerant passes through a compressor where the refrigerant is pressurized, raising its temperature to over 180 degrees F. The hot gas then circulates through a refrigerant-to-air heat exchanger where heat is removed as the cooler return air passes over it. Now heated, this warm air is delivered into the building by way of the blower and the duct system. Upon releasing its heat energy into the air, the refrigerant returns to the water-to-refrigerant heat exchanger where the process is repeated continuously during the heating process. A by-product of the heating function is the production of hot water that is delivered to the water heater by way of a small pump.
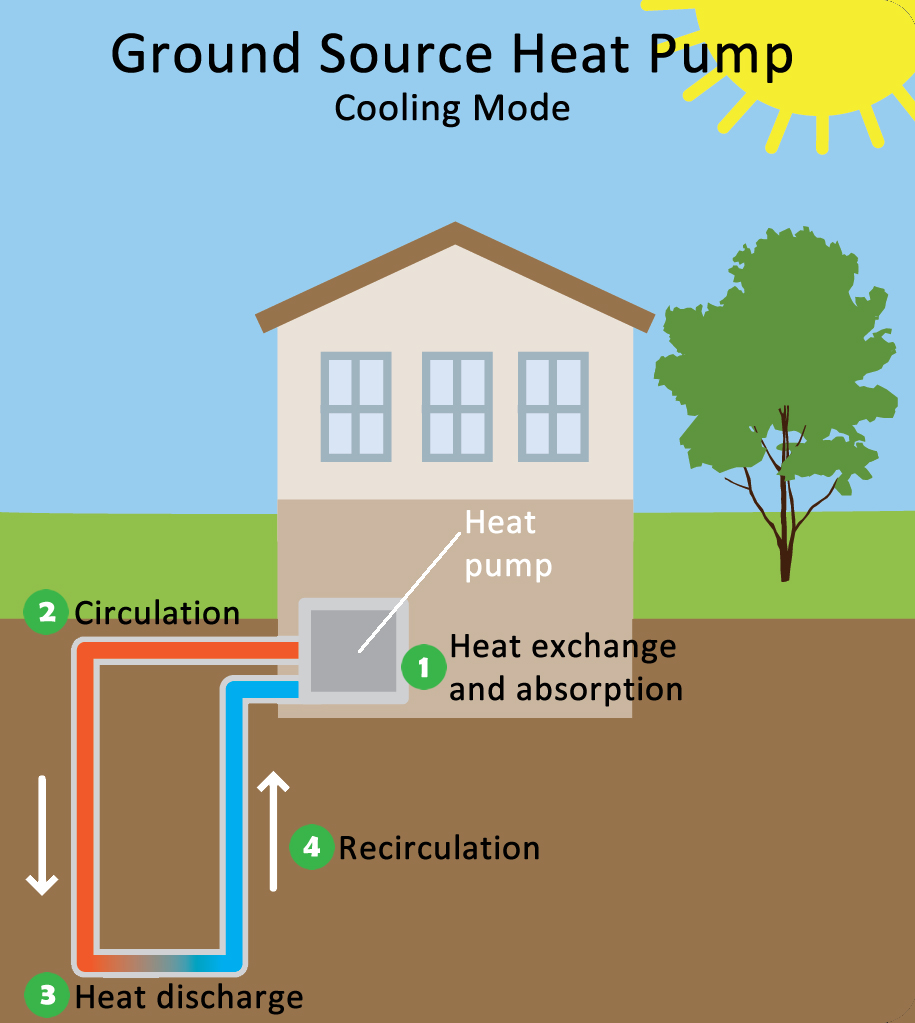
Geothermal - Cooling Mode
The cooling process involves the extraction of heat energy from the air in the building, and moving it into the earth. Transferring the heat from the air in the building to the earth involves a cycle of expansion, condensation, compression, condensation and evaporation. A refrigerant is used as the heat transfer medium. The cooling cycle starts as the compressor delivers refrigerant to the water-to-refrigerant heat exchanger. Heat from the refrigerant is absorbed by (rejected into) the low temperature source (earth loop fluid or well water) resulting in the refrigerant turning cold. The cold refrigerant passes through a refrigerant-to-air heat exchanger. As warm, humid air from the return air duct system is passed over the cold air coil, the air is cooled and dehumidified then returned into the building, cooling the space. The heat from the warm air that returns to the unit is absorbed by the cold refrigerant, turning the refrigerant into a hot gas. The hot refrigerant is returned to the compressor where the process is repeated continuously during the cooling process. A portion of the heat returning to the compressor (from the hot return air) is diverted to another refrigerant circuit that generates hot water and delivers it to the water heater by way of a small pump.
F.A.Q.
How will I save money with geothermal heating and cooling?
How much space does a geothermal unit require?
How long will my geothermal system last?
How effective is this underground system?
Are geothermal systems guaranteed?
How noisy is the unit?
Geothermal heating and cooling systems are very quiet, providing a pleasant environment inside & outside of the home. The systems have no noisy fan units to disturb outdoor activities, on or near the patio.
How safe are Geothermal heating and cooling systems?
Geothermal heating and cooling systems are safe and protected. With no exposed equipment outdoors, children or pets cannot injure themselves or damage exterior units. The systems have no open flame, flammable fuel or potentially dangerous fuel storage tanks.
Does my state offer any incentives for installing a geothermal heating cooling system?
Some utilities offer rebates or incentives to their customers who purchase GSHPs. To see what your state has to offer click here.
About Solar
In the broadest sense, solar energy supports all life on Earth and is the basis for almost every form of energy we use. The sun makes plants grow, which can be burned as “biomass” fuel or, if left to rot in swamps and compressed underground for millions of years, in the form of coal and oil. Heat from the sun causes temperature differences between areas, producing wind that can power turbines. Water evaporates because of the sun, falls on high elevations, and rushes down to the sea, spinning hydroelectric turbines as it passes. But solar energy usually refers to ways the sun’s energy can be used to directly generate heat, lighting, and electricity.